Sitting Chair Styles
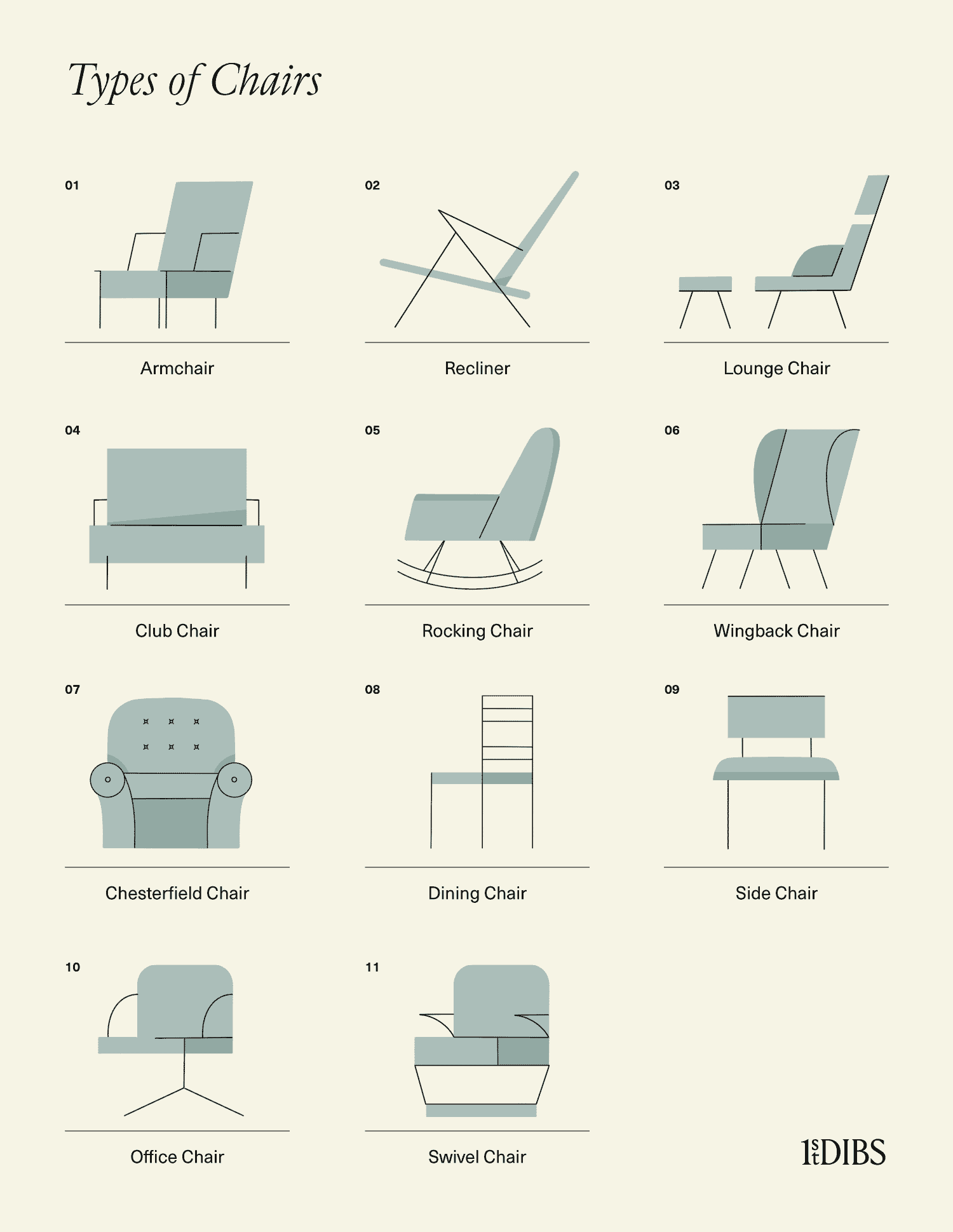
The realm of seating furniture is vast and varied, encompassing an extensive array of designs meticulously crafted to fulfill diverse functional, aesthetic, and ergonomic requirements. These essential pieces of furniture are more than mere objects for repose; they are integral components of interior design, dictating comfort, supporting posture, and contributing significantly to the overall ambiance of any space. From the bustling corporate environment to the intimate domestic setting, the choice of an appropriate seating solution profoundly impacts productivity, well-being, and visual appeal. Understanding the nuances of different designs allows for informed selections that enhance both functionality and style.
The evolution of seating has mirrored societal advancements, technological innovations, and shifts in artistic sensibilities. What began as simple stools has transformed into complex ergonomic marvels and elaborate decorative statements. Each design possesses unique characteristics, materials, and historical origins that contribute to its distinct identity and purpose.
Functional Categories and Distinct Designs
Seating solutions can be broadly categorized based on their primary function, each category featuring numerous specialized designs.
Office and Task Seating
Designed for productivity and prolonged periods of work, office and task chairs prioritize ergonomics and adjustability.
- Ergonomic Chair: This design is engineered to support the human body’s natural posture, offering extensive adjustability for height, back angle, lumbar support, armrests, and seat depth. Its primary benefit is the prevention of musculoskeletal issues and the promotion of sustained comfort during long working hours.
- Executive Chair: Often characterized by its larger size, high back, and luxurious materials such as leather, the executive chair projects authority and status. While offering comfort, its design emphasizes aesthetic grandeur and a commanding presence within a professional setting.
- Task Chair: A more compact and versatile option, the task chair provides essential adjustability for various office tasks. It is typically less elaborate than an executive chair but offers sufficient support for day-to-day work, making it suitable for a wide range of users and office layouts.
- Conference Chair: Designed for meeting rooms, these chairs balance comfort with a professional appearance. They often feature sleek designs, moderate adjustability, and materials chosen for durability and ease of maintenance in high-traffic environments.
- Drafting Chair: Distinguished by its elevated height and foot ring, the drafting chair is used with drafting tables or standing desks, allowing users to work comfortably at higher surfaces while maintaining good posture.
Dining Seating
Dining chairs are crafted to provide comfort during meals and complement the dining table’s aesthetic.
- Side Chair: This is a backless or armless chair, designed to be easily moved and to fit compactly around a dining table. Its minimalist form allows for maximum seating capacity and an unobstructed view.
- Arm Chair (Dining): Featuring armrests, these chairs offer enhanced comfort and a more formal feel. They are often placed at the head of a dining table as host chairs, providing a sense of prominence.
- Parsons Chair: A contemporary classic, the Parsons chair is fully upholstered, featuring a simple, clean silhouette with straight lines and no exposed wood frame. Its versatility allows it to blend with various dining room styles.
- Windsor Chair: A timeless design, the Windsor chair is characterized by its turned legs, spindle back, and often a saddle-shaped seat. Its rustic charm and sturdy construction have made it a enduring choice for casual and traditional dining spaces.
- Ladder-back Chair: Identified by its horizontal slats or “ladders” across the backrest, this design offers a classic, often rustic, aesthetic. It is known for its durability and simple elegance.
Lounge and Living Area Seating
These furniture pieces are primarily intended for relaxation, socializing, and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of living spaces.
- Armchair: A quintessential piece of living room furniture, the armchair features a single seat with armrests, offering a comfortable and often decorative seating option for individuals.
- Club Chair: A generously proportioned, upholstered armchair with deep seating and often low arms, the club chair exudes comfort and a relaxed, luxurious feel, often associated with traditional gentlemen’s clubs.
- Wingback Chair: Distinguished by its “wings” extending from the backrest down to the armrests, the wingback chair originally served to protect occupants from drafts. Today, it is valued for its stately appearance and enveloping comfort, often serving as a focal point.
- Recliner: Engineered for ultimate relaxation, the recliner allows the backrest to tilt backward and a footrest to extend forward. Modern versions often include features like heat, massage, and power adjustments.
- Chaise Lounge: A long upholstered chair designed for reclining, supporting the legs. It combines the functions of a chair and a daybed, ideal for relaxation and adding a touch of elegance to a room.
- Slipper Chair: An armless, low-seated upholstered chair, the slipper chair is designed for ease of use in smaller spaces or for tasks like putting on shoes. Its compact form and elegant lines make it a versatile accent piece.
- Barrel Chair: Named for its rounded, barrel-like backrest that often continues into the arms, this chair offers a cozy and enveloping seating experience, suitable for both modern and traditional interiors.
- Accent Chair: A broad category for decorative chairs chosen primarily for their aesthetic appeal and ability to complement or contrast with existing furniture, adding visual interest and a pop of color or texture.
Occasional and Specialized Seating
This category includes furniture pieces designed for specific, less frequent uses or particular environments.
- Rocking Chair: Featuring curved bands (rockers) attached to the bottom of its legs, allowing the occupant to rock back and forth. It is synonymous with comfort, relaxation, and often evokes a nostalgic sentiment.
- Adirondack Chair: An outdoor classic, the Adirondack chair is characterized by its wide armrests, slanted back, and low seat. Typically made of wood, it is designed for leisure and offers a comfortable, laid-back posture ideal for enjoying nature.
- Stools (Bar and Counter): These elevated seating options are designed for use at bars, kitchen islands, or high counters. Bar stools are taller than counter stools, and both come in various designs, from backless to full-back with armrests, offering functional seating in casual dining or entertaining areas.
- Bean Bag Chair: An unstructured chair filled with small polystyrene beads, conforming to the body’s shape. It offers a highly informal and adaptable seating solution, popular in casual living spaces and children’s rooms.
Design and Material Influences
The aesthetic and functional characteristics of seating are heavily influenced by the materials used in their construction and the design movements they represent.
Materials:
- Wood: A traditional and versatile material, wood offers durability and a timeless aesthetic. Hardwoods like oak, walnut, and cherry are prized for their strength and grain patterns, while softer woods like pine are used for more rustic or painted finishes.
- Metal: Steel, aluminum, and wrought iron are employed for their strength, sleek appearance, and ability to be molded into various forms. Metal frames can offer an industrial, modern, or even ornate aesthetic.
- Plastic: Modern manufacturing techniques allow for plastic to be molded into ergonomic and visually striking forms. It is lightweight, durable, and available in a wide spectrum of colors, making it suitable for contemporary and outdoor applications.
- Upholstery: Fabric, leather, and synthetic materials like velvet, linen, and microfiber provide comfort, texture, and color. Upholstered pieces offer a soft seating experience and contribute significantly to a room’s decorative scheme.
Design Eras and Movements:
- Traditional: Designs from eras like Victorian, Colonial, or French Provincial often feature intricate carvings, ornate details, and rich fabrics, reflecting historical elegance and formality.
- Modern: Encompassing movements like Mid-Century Modern, this style emphasizes clean lines, functional forms, and a rejection of excessive ornamentation. Materials often include wood, metal, and simple upholstery.
- Minimalist: Characterized by simplicity, functionality, and a ‘less is more’ approach, minimalist designs feature uncluttered lines, neutral palettes, and essential forms.
- Industrial: Drawing inspiration from factories and urban lofts, industrial designs incorporate raw materials like exposed metal, reclaimed wood, and utilitarian forms, often featuring a rugged, unfinished look.
- Transitional: This style blends elements of traditional and modern design, creating a balanced aesthetic that is both classic and contemporary, offering versatility in various interior settings.
Importance and Benefits of Diverse Seating Options
The availability of a wide range of seating options is not merely a matter of aesthetic choice; it underpins numerous functional and well-being benefits.
- Ergonomics and Health: Appropriately designed seating is crucial for maintaining good posture, supporting spinal alignment, and preventing musculoskeletal disorders. Ergonomic designs, in particular, are engineered to reduce strain, improve circulation, and minimize fatigue, leading to better overall health and increased comfort.
- Aesthetics and Interior Design: Each unique seating design contributes to the visual narrative of a space. Chairs can serve as focal points, define zones within an open plan, or seamlessly blend into the existing decor. The choice of form, material, and color significantly impacts the mood and style of an environment, reflecting personal taste or corporate branding.
- Functionality and Adaptability: Different activities demand specific seating solutions. A task chair facilitates focused work, a dining chair promotes comfortable meal consumption, and a lounge chair encourages relaxation. The diversity of available designs ensures that there is an optimal solution for every function, enhancing the efficiency and enjoyment of various activities.
- Durability and Longevity: The selection of materials and construction methods directly influences the lifespan of seating furniture. High-quality materials and robust craftsmanship ensure that pieces withstand daily use, offering long-term value and reducing the need for frequent replacement.
- Space Optimization: Specific designs are tailored for different spatial constraints. Compact side chairs or armless options can maximize seating in smaller areas, while larger, more elaborate pieces can anchor expansive rooms. Thoughtful selection allows for efficient use of available space without compromising comfort or style.
The comprehensive array of seating options available today reflects centuries of innovation and adaptation. Each design serves a distinct purpose, combining form and function to create furniture that is both practical and aesthetically pleasing. The careful consideration of these varied forms ensures that every environment can be equipped with seating that perfectly meets its specific demands for comfort, style, and utility.
FAQs by sitting chair styles
What criteria determine the classification of various designs?
Classification is primarily determined by the intended function, design elements (such as the presence of arms, back height, or upholstery), typical placement within an environment, and the materials used in construction. Historical context and prevalent aesthetic movements also play a significant role.
How do ergonomic designs differ from standard designs?
Ergonomic designs are specifically engineered to support the human body’s natural posture and movements, often featuring extensive adjustability in multiple components (e.g., seat height, back angle, lumbar support, armrests). Standard designs may offer comfort and aesthetic appeal but typically lack the comprehensive adjustability and scientific backing for prolonged postural support found in ergonomic models.
Can designs influence productivity in a workspace?
Yes, the choice of design significantly impacts productivity. Ergonomically designed options that provide proper support and comfort can reduce physical discomfort and fatigue, allowing individuals to concentrate more effectively on tasks. Conversely, poorly designed seating can lead to discomfort, pain, and reduced focus, negatively affecting work output.
What considerations are paramount when selecting designs for a dining area?
Key considerations include the size and shape of the dining table, the available space, the number of individuals to be accommodated, and the overall aesthetic of the dining room. Comfort for extended meal times, durability of materials, and ease of cleaning are also crucial factors.
Are there universal designs suitable for multiple environments?
While some designs exhibit versatility, truly universal designs are rare. Most options are optimized for specific functions or environments. For example, an accent chair can fit in various rooms for decorative purposes, but it may not be suitable for prolonged desk work or formal dining. Specific functional requirements often necessitate specialized designs.
Tips by sitting chair styles
- Prioritize Ergonomics for Prolonged Use: When selecting for workspaces or areas where extended periods of sitting are anticipated, prioritize designs with robust ergonomic features. This investment supports health and enhances long-term comfort and productivity.
- Assess Material Durability and Maintenance: Consider the environment and expected usage. High-traffic areas benefit from durable, easy-to-clean materials like leather or performance fabrics. Outdoor environments require weather-resistant options such as treated wood, aluminum, or synthetic weaves.
- Match Design to Room Scale: Ensure the chosen design is proportionate to the room size. Oversized pieces can overwhelm a small space, while undersized ones may appear lost in a large room. Proper scale contributes to visual balance and functional flow.
- Consider Multi-functional Designs for Small Spaces: In environments with limited square footage, explore designs that offer multiple functions, such as ottomans with storage or compact armless chairs that can be easily repositioned, maximizing utility without clutter.
- Test for Personal Comfort: Whenever possible, physically test a design before purchase. Individual body types and comfort preferences vary significantly. A design that is highly rated may not be suitable for every person.
Conclusion by sitting chair styles
The extensive variety of seating furniture available today underscores its fundamental role in human environments. Each distinct design, from the ergonomically Benny Harlem Hair Products A Comprehensive Guide To Natural Hair Care Excellence advanced office chair to the decorative accent piece, is a testament to centuries of evolving needs and aesthetic preferences. The deliberate selection of these crucial furniture items extends beyond mere utility, profoundly influencing comfort, health, productivity, and the overarching ambiance of a space. An informed understanding of the characteristics, materials, and intended functions of different designs empowers individuals and organizations to make choices that optimize both practical requirements and visual appeal. This thoughtful approach ensures that every seated experience is as supportive and aesthetically pleasing as possible, affirming the enduring significance of well-chosen seating solutions.






More suggestion: V Shape Hairstyle For Man A Comprehensive Guide To Modern Masculine Aesthetics